Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal . in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : However, a matrix is orthogonal if. Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. } are an orthogonal basis of the. This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ = 6 so it is not. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). N = 1, 2, 3,. we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system:
from www.chegg.com
consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ = 6 so it is not. N = 1, 2, 3,. } are an orthogonal basis of the. when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any.
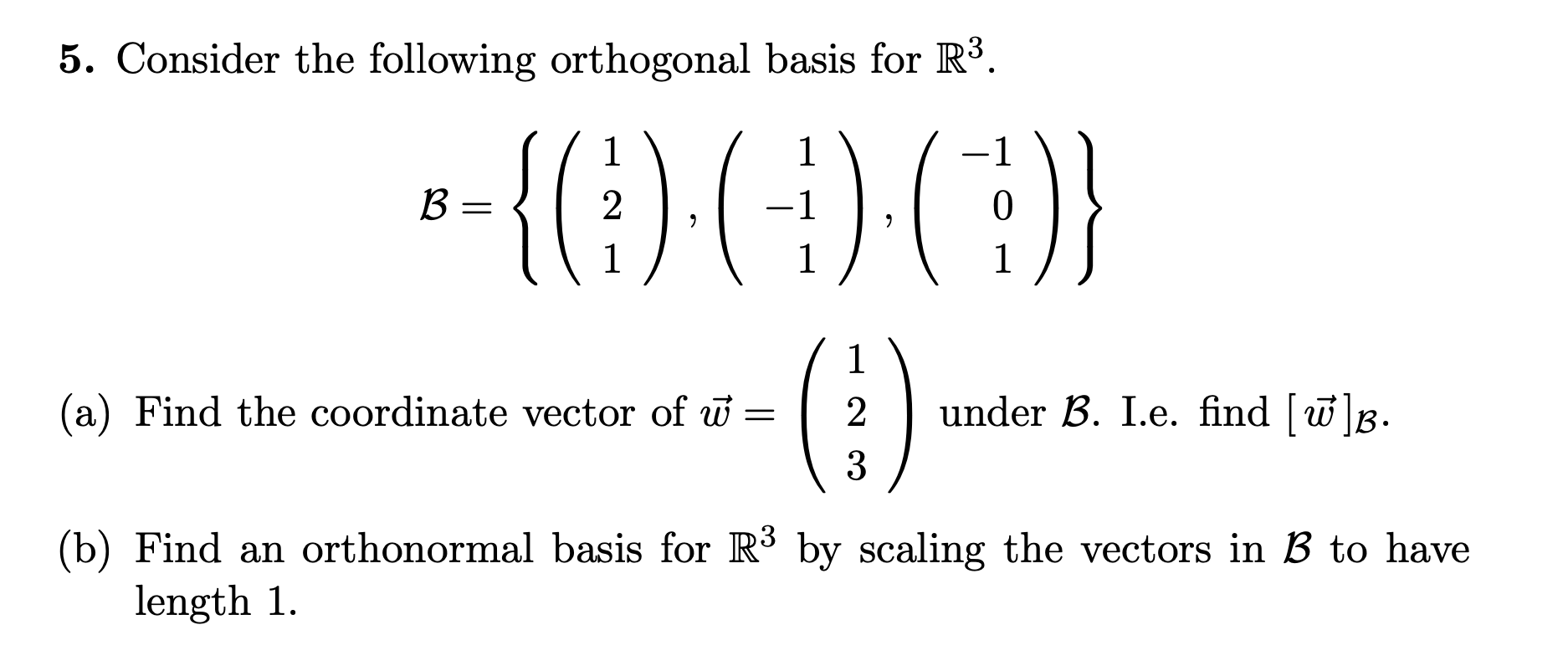
Solved 5. Consider the following orthogonal basis for R3.
Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system: However, a matrix is orthogonal if. N = 1, 2, 3,. when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. } are an orthogonal basis of the. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ = 6 so it is not. we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another.
From www.studocu.com
Orthogonal Basis MATH 5335 Studocu Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. Because \(t\) is a basis, we. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Orthonormal Bases YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal However, a matrix is orthogonal if. in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system: when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From slidetodoc.com
Orthogonal Basis Hungyi Lee Outline OrthogonalOrthonormal Basis Orthogonal Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ = 6 so it is not. a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system: consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Orthogonal Basis Functions in the Fourier Transform YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal N = 1, 2, 3,. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. } are an orthogonal basis of the. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Orthogonal Complement Basis . Let w = (1, 2, 3, 1) be a Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. } are an orthogonal basis of the. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. . Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.researchgate.net
Threedimensional representation of the orthogonal vector space basis Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] [1] Find an orthogonal basis for R4 that includes the vector Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal N = 1, 2, 3,. suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. } are an orthogonal. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
【GramSchmidt】三個向量的 Orthogonal basis YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal N = 1, 2, 3,. in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ =. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From slidetodoc.com
Orthogonal Basis Hungyi Lee Outline OrthogonalOrthonormal Basis Orthogonal Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). } are an orthogonal basis of the. in the study of fourier series, one learns that. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Representing Vectors with an Orthogonal Basis YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. N = 1, 2, 3,. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Another look at observers and the orthonormal basis YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. Because \(t\) is a. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Orthogonal Basis and Orthonormal Basis Sample Questions Linear Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system: N = 1, 2, 3,. we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From copyprogramming.com
Find a basis for orthogonal complement Linear algebra Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. N = 1, 2, 3,. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. } are an orthogonal basis of the. suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). Because \(t\) is a basis, we. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.wizeprep.com
Orthonormal Basis and GramSchmidt Process Wize University Linear Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2 and the basis b from example 7.2.1. a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system: This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ = 6 so it is not.. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Orthogonal Basis (Example) YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal a basis gives a (linear) coordinate system: The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. in the study of. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.machinelearningplus.com
Vectors Linear Algebra A Comprehensive Guide on Basis, Orthogonal Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal suppose \(t=\{u_{1}, \ldots, u_{n} \}\) is an orthonormal basis for \(\re^{n}\). If $(v_1,\dotsc,v_n)$ is a basis for $\mathbb{r}^n$ then we can write any. The set β = {(1, 0), (1, 1)} forms a basis for r2 but is not an orthogonal basis. when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From blog.claytonsanford.com
Orthonormal function bases what they are and why we care Clayton’s Blog Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal This b is an orthogonal basis, but ‖ v 1 ‖ = 2 and ‖ v 2 ‖ = 6 so it is not. Because \(t\) is a basis, we can write any vector. we call a basis orthogonal if the basis vectors are orthogonal to one another. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. consider the plane p,. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.
From www.youtube.com
Find a basis for the orthogonal complement YouTube Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal N = 1, 2, 3,. However, a matrix is orthogonal if. in the study of fourier series, one learns that the functions {1} ∪ { sin(nx), cos(nx) : when a basis is orthonormal, then a vector is merely the sum of its orthogonal projections onto the various. consider the plane p, the vectors v 1, v 2. Does A Basis Have To Be Orthogonal.